Origins to Innovation: Cloud Computing's Impact on HR
Do you know why it's called cloud computing and are you aware of the benefits to HR?
- 06 Jun 2024
- Max 11 min read
The Number One HR Solution on Salesforce
Absenteeism can cause workplace disruption and it is important for employers to be aware of its impact. But there are methods to track absenteeism. The Bradford Factor could be just the formula you need to identify and solve attendance issues.
The Bradford Factor score is a tool human resource departments use in absence management. Its formula helps you understand employee absences and their impact on your business. It takes into account short-term absences as well as long-term absences.
The Bradford Factor was created as part of research conducted by the University of Bradford School of Management in the 1980s. The theory concluded that shorter unplanned absences are more disruptive to a business than longer absences.
The goal of absence management is to give people the time off they need, while still maintaining productivity. Bradford Factor triggers are used as a basis to understand when the absences of an employee become problematic and require actions to be taken.
The Bradford Formula is composed of two elements: the total number of absence instances or spells over a set period of time (S) and the total number of days the individual was absent during the given period (B).
The Bradford score is calculated with the formula:
S x S x D = B
So now let’s look at how to understand the result of the Bradford Factor score.
The lower the Bradford Factor score, the better for your business. Higher scores indicate a bigger negative impact on the organization. Let’s take a look at some examples:
An employee was absent for 10 days over the course of a 52-week period and all of these absence days occurred in one block. Their Bradford Factor score would be: (1 x 1) x 10 = 10
If an employee is absent twice in one year for five days at a time, their Bradford Factor score is: (2 × 2) x 10 = 40
If an employee is absent 10 times in 52 weeks for one day at a time, their Bradford Factor score is: (10 × 10) x 10 = 1,000
In these three scenarios, the employee has been absent for the same number of days in total. However, shorter, more frequent absences result in a higher Bradford Factor score. Based on this theory, there are benchmarks that can be used to compare employee scores.
While treating your employees the same way with a given formula might seem fair, that may not be the case because no two people are the same. Let’s explain this statement by taking a closer look at the examples from above and adding a use case to them.
Angela who is absent for 10 days in a row could be a person who had a rough case of the flu. This employee has a Bradford Factor of 10, which is very low.
Adam took six days off in a row last month. His Bradford Factor was (1 x 1) x 6, which equals a very low score of six. No cause for concern.
But Becca took one day sick per month for six months because of a known medical condition – perhaps she suffers from chronic migraine attacks that leave her unable to work for around 24 hours. She takes medication every day, but the medication doesn't always prevent an attack. Her Bradford score would be (6 x 6) x 6, which equals 216. According to the benchmarks, Becca’s score may require action.
It’s important to note that context matters with the Bradford Factor formula. Bradford scores may require a lot of context behind them. A Bradford Factor score alone is not an indicator of how “good” or “bad” an employee is. It can be used as an indicator to determine where you may need to take action, but you should always take context into account before making any decisions.
So why would one use the Bradford Factor?
Efficiency: The basic idea of using the Bradford Formula is to quickly get an overview of the absenteeism of employees. That way absences can be treated in an objective way, which can (as shown above) be a disadvantage as well as an advantage.
The score takes away an employer’s subjectivity. No one can accuse you of taking action against them or someone else just because you dislike them. Using a mathematical formula quantifies absences and gives you solid evidence.
Communication: It has been known to enhance communication between management and employees by providing clear guidelines for what constitutes acceptable absence levels. Ultimately, the Bradford Factor can help organizations better maintain employee attendance records while encouraging healthy working practices.
Reduced absence: One could also claim that the Bradford Factor motivates people to be more careful about their absences and only take time off when it is absolutely necessary.
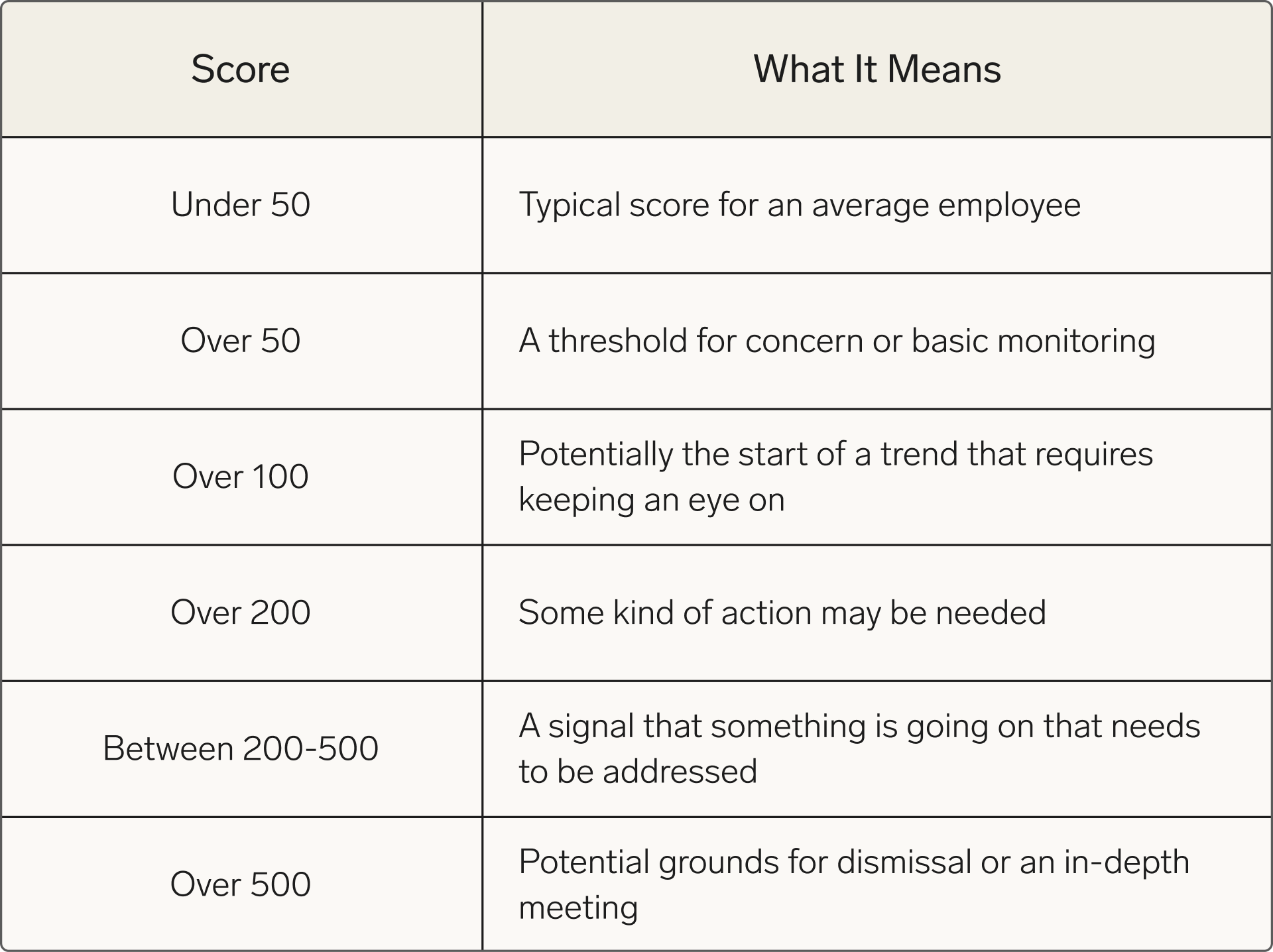
Typically companies have something called a “trigger point”, which is the maximum number of points an employee can accumulate before an action is taken. Here’s an example of how those trigger points could look:
Using trigger points makes sure you have a threshold for absences. However, employees might have medical conditions, disabilities, mental health problems, or family members who have one or more of those, and are likely to need more time off than the average employee. So be sure to take other elements into account.
For this reason, it would not be fair to take action based on this table. A more diverse approach to using the Bradford Factor score in HR could be to adapt trigger points for your employees.
In general, it is recommended to define a fair procedure for absences. This should also be available to employees in your absence management policies.
Bradford Factor trigger points should be treated as a guide, rather than a rule. It’s important to be fair to employees with disabilities or medical conditions, which may involve careful consideration of their performance and confidential record retrieval when dealing with their medical information. Understanding the context helps you make more informed decisions.
Sick leave is not a crime. We should not forget this when talking about efficiency topics. That’s why it’s important to build a culture where employees who are genuinely sick are supported and illegitimate absences are not tolerated. A good way of dealing with this is to have a dialogue with your employees. It’s better to communicate more, rather than less.
Return-to-work interviews can be a good opportunity to learn more about the absence of your employee. Maybe there are ways you can help that person to get fit again. Knowing the reason can help you understand where that person might need support. In the end, you want to have healthy, motivated, and engaged employees.
Absence management requires training and guidance. Managers handling absences should be trained to identify and react to repeated absences in a compassionate way. That way, employees can be given appropriate support before preventative absenteeism sets in. Early signs of decreased employee engagement could be:
Reading these signs can help you improve a situation before the Bradford Factor score even becomes relevant.
The Bradford Factor score has the potential to be a useful element in an absence management strategy, but one must take other factors into account before implementing any corrective action.
Carefully examining individual circumstances and utilizing employee engagement surveys can help prevent adverse outcomes caused by unintentional discrimination of employees suffering from medical conditions, for example. A well-defined absence policy is key to setting expectations in the workplace.
It's important that employers, HR departments, and employees know how absenteeism should be handled – what types of absences are permissible, when notice needs to be given, and how it must be communicated. Once everyone knows where they stand, then the Bradford Factor formula can be a handy addition to any healthy absence management strategy.
For more information about how the flair HR software can assist absence management, check out our product pages here.
Join flair’s newsletter to receive the latest tips & trends in the HR world.