Origins to Innovation: Cloud Computing's Impact on HR
Do you know why it's called cloud computing and are you aware of the benefits to HR?
- 06 Jun 2024
- Max 11 min read
The Number One HR Solution on Salesforce
The number of part-time employees continues to rise, especially in affluent countries. As of February 2023, there were 27.54 million part-time workers in the United States. Part of the reason for this trend is that many people are choosing to give up some of their income in favor of flexibility and a better work-life balance.
While part-time workers can be beneficial to companies, they also present some challenges. HR managers and project managers who are responsible for staffing need a reliable way to calculate how many employees are needed and how many are available. To do this, they use a specific unit of measurement known as full-time equivalent (FTE). This is an essential metric for businesses that employ full-time and part-time workers as it makes the two comparable in different contexts. Let’s take a closer look.
Full-time equivalent or FTE is a unit of measurement to determine the workload of part-time and full-time employees. It converts the working hours of part-time staff into a comparable full-time value. It’s a very useful metric for companies with staff members who have a variety of different working hours per week.
For example, a team made up of 10 part-time employees will work fewer hours than a team of eight full-time workers. And this is where FTE comes into play. Instead of comparing employee numbers, FTE helps HR teams to measure the total number of hours worked. This is beneficial in staffing and capacity planning for projects. A higher FTE means more human resources.
Besides hiring considerations, FTE is often used in budgeting. In project-based work, FTE calculation is essential to figure out the labor costs and total hours needed to complete a certain task. The FTE equates to the number of full-time employees that would be needed to complete the project.
Using a simple formula, you can calculate your company’s FTE to make more accurate forecasts compared to a basic headcount.
It is very common for companies to employ staff on a variety of different contracts. Large enterprises and small businesses alike can become more flexible by hiring people for part-time positions, internships, and apprenticeships, alongside full-time roles. Without calculating the full-time equivalents, these different working models can make it difficult to forecast capacity and staffing needs.
Using FTE as a metric gives businesses a more accurate picture of their capacity. While a normal headcount only provides the number of employees contracted by a company, the FTE shows the number of full-time hours the workforce is capable of performing per week.
Knowing the FTE of your staff makes it easier to fairly compare the performance of full-time and part-time employees. Using this value, you can forecast how much work a part-time member of staff can be expected to perform compared to a full-time equivalent employee.
If there is a significant difference between the expected performance and actual results, it may be a good reason to schedule a staff appraisal. During this meeting, you could find out what support the member of staff needs to meet requirements and discuss training courses that might improve performance.
It may be necessary to calculate your company’s FTE for health insurance and tax reasons. In some countries, companies are required to meet certain requirements once they employ a specific number of FTEs. For example, in the United States, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires employers with 50 or more FTEs to offer certain ACA-compliant healthcare benefits.
To figure out the total FTE of all full-time and part-time employees, HR managers use a simple formula. The company’s total FTE is equal to the total number of hours worked by part-time and full-time employees divided by the total number of full-time hours over the same period.
To calculate the total number of full-time hours in a year, you would multiply the working hours per day by the working hours per week. Then you would multiply that number by 52, the number of weeks in a year. Based on a 40-hour workweek, this would be:
8 (hours per day) x 5 (days per week) x 52 (weeks per year) = 2,080 hours
So 2,080 hours of work in a year is equal to one FTE.
To calculate the FTE value of part-time employees, you take the number of part-time work hours over a specific period of time and divide that number by the work hours in a full-time schedule. So if a full-time work schedule for a week is 40 hours, an employee who works 20 hours per week counts as 0.5 FTE (20 divided by 40).
A good starting point for calculating your company’s FTE is to track the actual number of hours your employees work, especially if you offer flexible working hours. With HR software like flair, you can use a time tracker to keep a record of the total hours worked by full-time and part-time employees. It gives you and your staff a clear overview of weekly hours and can even be integrated with physical devices to automatically clock in and clock out employees.
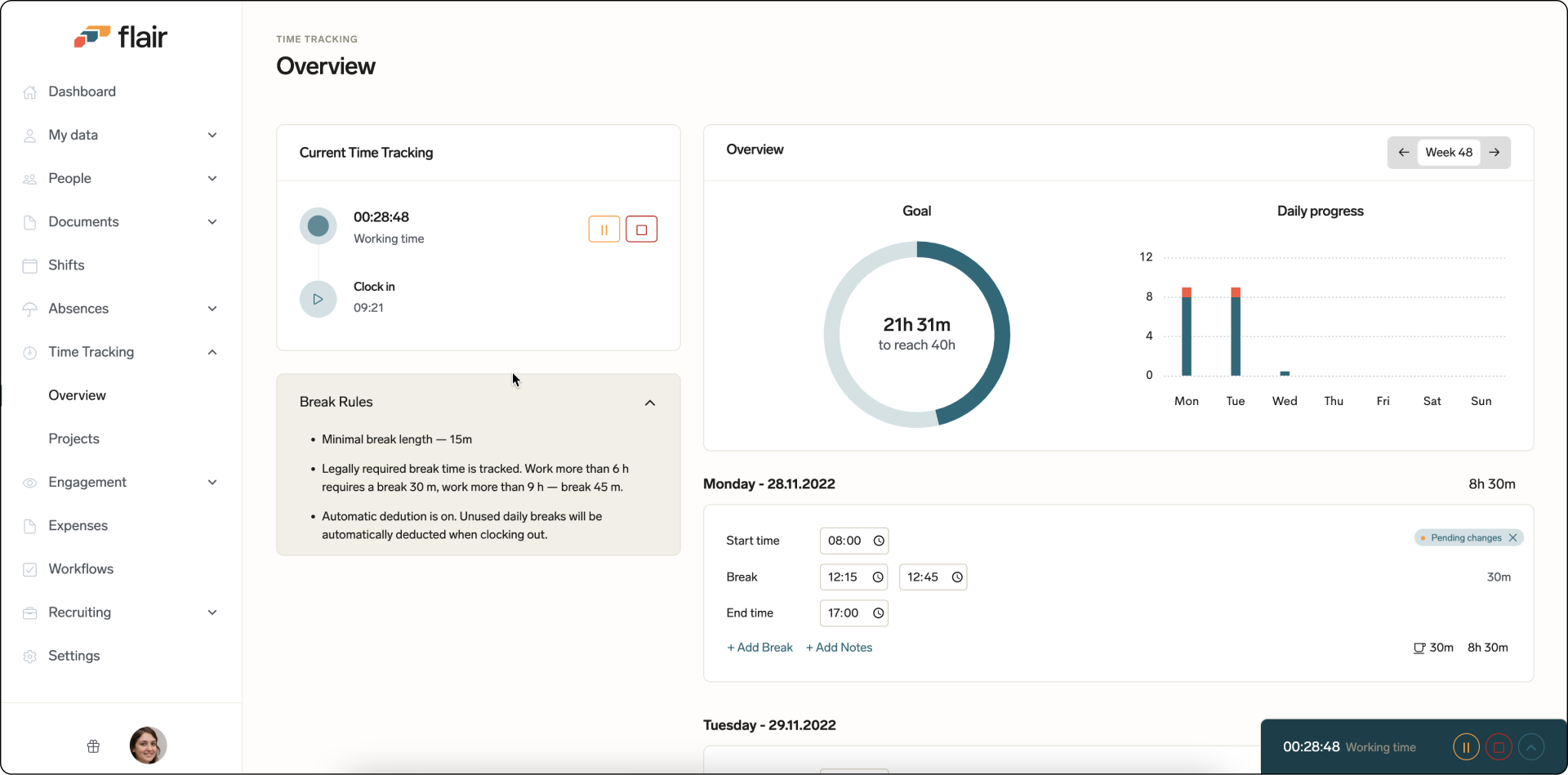
Imagine a company employing 30 people. Of these 30, there are 20 full-time workers who work 40 hours per week and 10 part-time workers who work 25 hours per week.
First, you need to find the FTE of the 10 part-time workers. To do this, you divide their weekly working hours (25) by the number of hours in a full-time workweek (40). The result is an FTE of 0.625. So 10 part-time workers have an FTE of 0.625 x 10 = 6.25.
The 20 full-time employees are equal to 20 FTE. So when you add the full-time and part-time staff together, you have a total FTE of 26.25.
This calculation helps HR managers to plan staff shifts and distribute working hours across part-time and full-time positions. Instead of using a simple headcount, planning and budgeting are based on actual working hours. Besides weekly shift planning, FTE also helps companies to recruit in the right areas depending on the workload.
It can also help you to determine the wage that part-time workers should receive. You simply multiply the full-time wage by the FTE of the part-time employee. Sticking with the example above, where a full-time employee works 40 hours per week and a part-time employee works 25, a part-time employee has an FTE of 0.625. If a full-time employee earns €50,000 per year, an employee working 25 hours per week should earn 50,000 x 0.625 for the same job. This equals €31,250.
One of the biggest benefits of FTE numbers is that they help you deploy full-time and part-time employees in an effective way. To figure out the FTEs needed for a project, you first need to estimate how many hours of work are required. Dividing this number by the hours in a full-time workweek will give you the number of FTEs required.
For example, let’s say you estimate that an upcoming project will take 300 hours to complete. If you have a standard 40-day workweek, the formula will be 300 ÷ 40 = 7.5. This means that 7.5 FTEs are required to finish the project in one week.
Let’s assume your part-time employees work 20 hours per week. To reach 7.5 FTEs and complete the project in one workweek, you could assign seven full-time employees and one part-time employee to the project. Alternatively, you could select five full-time employees and five part-time employees.
The world of work continues to change, and flexible working schedules have become an attractive benefit in the search for talent. Finding the right balance of full-time and part-time workers can also boost companies’ efficiency and help avoid overstaffing or understaffing.
Recruiting part-time employees can be a good way to strengthen a team during busy periods or provide cover for longer absences and sick leave. Offering part-time contracts also widens your talent pool while helping you retain employees who may want to reduce their working hours as they enter a new phase in their life.
If your company employs people on a variety of contracts with different workloads, it’s important to understand FTE as a unit of measurement. Not only can it help you to prioritize your hiring plans, but it is also useful in capacity planning, budgeting, performance management, and salary discussions. Even if your team works flexible hours, calculating your FTE can help you plan projects better and the right people for the job.
If you want to calculate your FTE count more precisely, flair can help you track your workforce’s working hours. Our time-tracking feature supports digital time tracking, time tracking with physical devices, and project-based time tracking. What’s more, our solution includes absence management, so you can take sick leave and vacations into account too.
flair helps you track and analyze important KPIs such as FTE, turnover rate, and time to hire. Use our Salesforce-powered solution to create standard and custom reports and dashboards to aid your decision making. Book a call to learn more.
Join flair’s newsletter to receive the latest tips & trends in the HR world.

